17 Tips to Improve Sleep and Hormonal Health
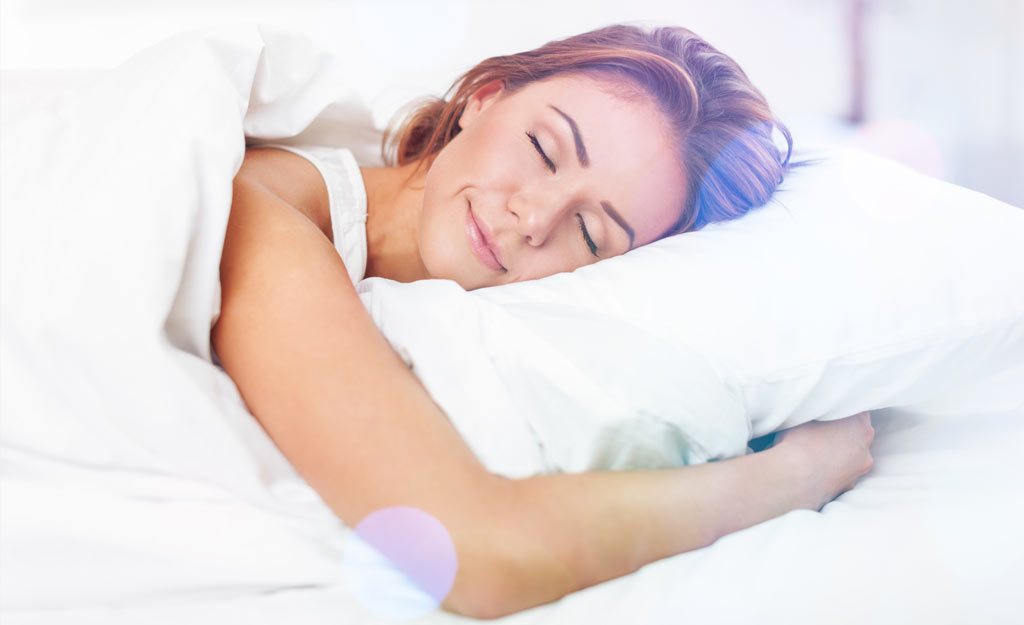
Sleep has an incredibly important role to play in hormonal health. If you're not sleeping well then there is a very high chance your hormonal balance is being affected.
The gland that controls our circadian rhythm (sleep cycle) is called the pineal gland. The pineal gland is the master controlling gland and regulates Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinising hormone (LH) via the pituitary gland, which are two very important hormones in regulating female hormonal cycles.
The pineal is a very small gland in the brain, yet very vascular, receiving vast amounts of blood only second to the kidneys - which shows how it regulates the balance of hormones circulating in the blood supply.
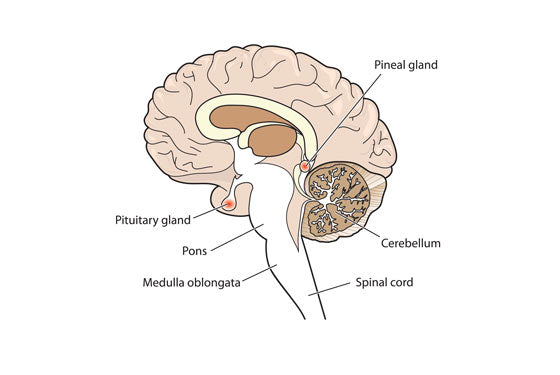
Now here is the key. The pineal gland also regulates sleep via melatonin and serotonin (both feel good hormones). When there is poor sleep or insufficient sleep the levels of these hormones drop, which influences the reproductive hormonal balance.
Interestingly during the first 6 months after childbirth, these hormones are elevated to assist mothers to go back to sleep while breastfeeding.
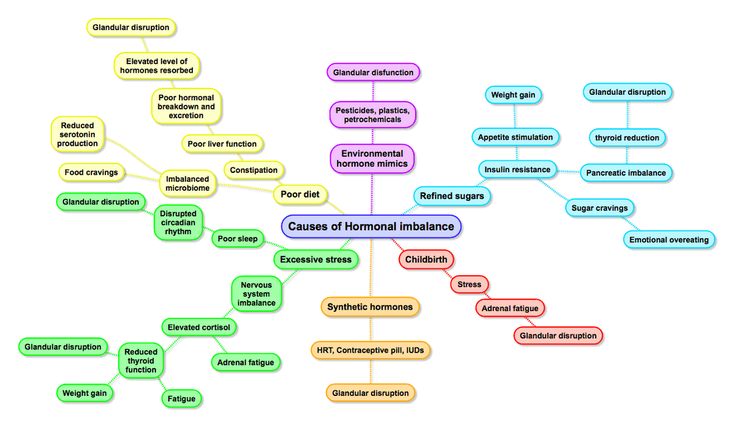
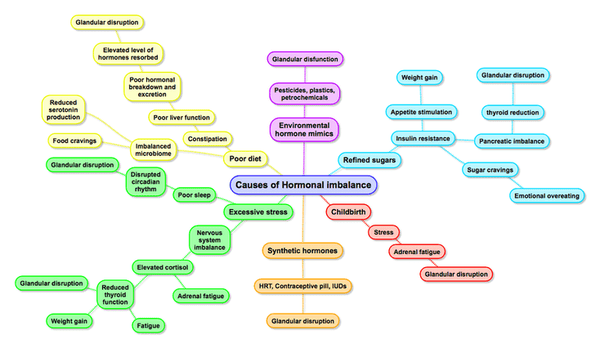
Sleep is the most important trigger for maintaining healthy biorhythms. The wake-sleep cycle, or circadian rhythm, triggers every other biorhythm to function correctly. Long-term disruption in the amount of sleep or the times of sleep will disrupt the circadian rhythm and hence a whole range of biorhythms, including the glandular system and consequently, hormonal levels.
The most profound effect from sleep is healing and repair. Daily activity creates a wealth of metabolic toxins, as well as from normal wear and tear. We accumulate stress and emotions in our muscles. Our bodies need to eliminate the physical and emotional toxins as well as repair any damaged tissues.
The reason we sleep is to conserve energy to be distributed into healing biochemical reactions such as repair and detoxification. When there is inadequate sleep, the body does not have the time or sufficient energy to perform these functions.
During sleep, a hormone is produced by the pineal gland called melatonin. Melatonin levels increase during sleep and are responsible for the sleep cycles.
Interestingly melatonin is a potent antioxidant. Antioxidants protect the body and assist in the healing and detoxification process. In a study of 82,000 nurses, it was found those who had six hours or less of sleep each night had a significantly increased risk of breast cancer. In separate research low levels of melatonin have also been linked to breast cancer.

When we wake in the morning our level of wellbeing and feeling of being refreshed depends upon our overall vitality. The more toxins which need eliminating, the worse you will feel in the morning.
Often you will not feel like eating until the body has fully eliminated the toxins released the night before. The word 'breakfast' comes from the root of 'breaking the fast'. This is why lemon juice in water is a great start to the day.
The quality of sleep is also an important issue. You may be getting eight hours, yet the sleep is disturbed and irritable. The level of mental or emotional stress plays a role here. The body can be likened to a piece of rope. During the day it gets twisted and twisted with mental and emotional stress. Unless this stress is released through exercise or relaxation, the piece of rope slowly unwinds during the night leading to a disturbed sleep.
In a study of 82,000 nurses, it was found those who had six hours or less of sleep each night had a significantly increased risk of breast cancer.
The quality of sleep is also related to the level of toxicity in the body and/or reactive foods. If there are high levels of toxins that need to be eliminated or reactive foods are being consumed, the body often has a restless or disturbed sleep.
The reason is the release of these toxins during the night has an irritating effect on the nervous system. This leads to disturbed sleep.
Most people eating a diet high in refined sugars, stimulants and junk food will recognise this phenomenon. Children who wet the bed, commonly have food intolerances or consume junk food & soft drinks during the day.
Recent research has discovered a lack of sleep increases stress hormone levels. Elevated stress hormones have multiple detrimental effects on the body. Heightened stress hormones reduce the output of sex hormones, which lessens communication with reproductive tissues, so they can no longer adequately maintain a healthy monthly cycle.
It is interesting to note lack of sleep increases stress hormones and increased stress reduces sleep.
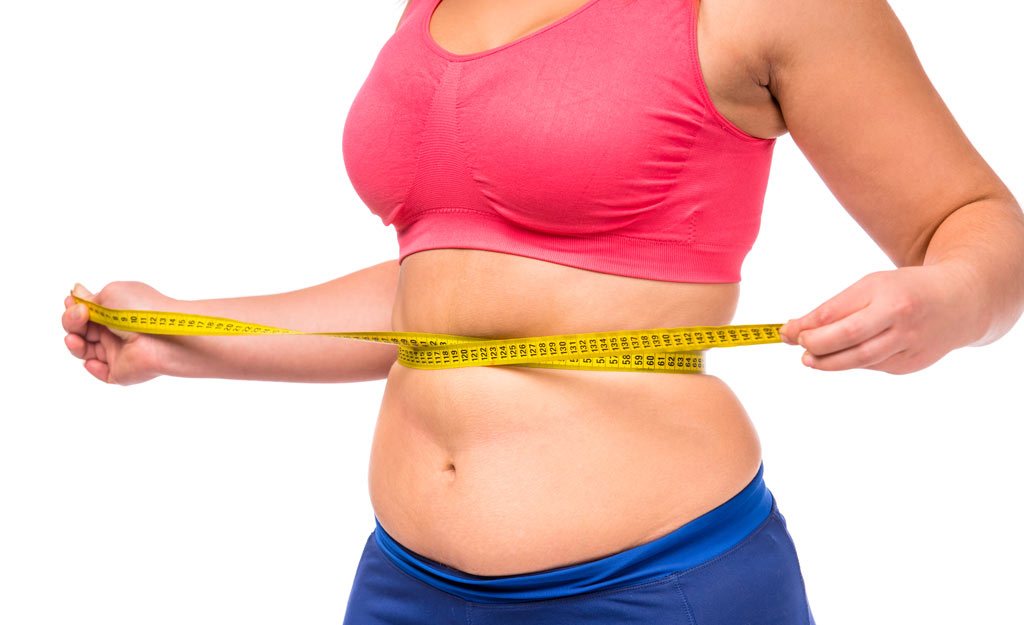
Long-term elevated stress hormones also reduce metabolism. Research has shown people who sleep less than 6 hours per night are more likely to be obese. Long-term elevation of stress hormones also disrupts blood sugar balance, which explains the increase of diabetes in people who sleep less than 6 hours a night.
Disrupted blood sugar levels is a contributing factor to obesity, and is a contributing factor to diabetes. Disrupted blood sugar levels and reduced thyroid function are both factors in hormonal imbalance.
It is interesting to note lack of sleep increases stress hormones and increased stress reduces sleep. It can be a vicious cycle and stress management is a key element in restoring balance.
The end result of poor sleep is reduced detoxification and repair, dysregulation of blood sugar, and elevation of stress hormones. These biochemical reactions lead to increased levels of inflammatory mediators. And increased long-term inflammation is the major precursor to all chronic disease, particularly cancer!!
How to get a good night sleep
- Exercise is the simplest and most effective way you can get a sound night's sleep. If you have a lot of mental activity or emotional stress during the day, exercise is essential to release this tension. Make certain you are exercising regularly. Exercising for at least 30 minutes every day can help you fall asleep. Don't exercise too close to bedtime, or it may keep you awake.
- Listen to relaxation CD's or listen to a guided relaxation. Stress is one of the biggest inhibitors of a healthy night's sleep.
- Avoid television before bed, and even better, remove the television from the bedroom. Television is too stimulating and disturbs the pineal gland function, which is needed to produce enough melatonin for a good night's sleep.
- Avoid eating your evening meal too late. Sleep may come quickly, however, if your blood sugar falls too low, you may wake up and have difficulty getting back to sleep. Avoid bedtime snacks for the same reason.
- Sleep in a room which is as dark as possible. Even small amounts of light can reduce the production of serotonin and melatonin. Also keep the light off when you use the bathroom.
- Avoid loud alarm clocks. It is stressful to be woken up suddenly. Ideally, you should wake slowly with the sun rising. If this is not possible, there are alarm clocks called sun alarms which slowly increase the amount of light in the room, allowing the circadian rhythm to adjust.
- Avoid caffeine. Caffeine and other stimulants obviously can keep you awake. Some people, however, do not metabolise caffeine until up to six hours later; so be aware an afternoon coffee may be keeping you awake.
- Try and go to sleep at a similar time each day. As you have learnt, the body is a creature of habit. If you go to sleep every night at 10 pm, your body will naturally produce serotonin and melatonin at this time, even if you may not have done all the right things beforehand.
- Wear socks to bed in a cooler climate. This prevents the body getting too cold and prevents waking up at night. Also, try and keep the temperature constant in the room to avoid overheating or cooling.
- Keep a journal. Recording the day's events can help to eliminate any stressors and help you plan for the next day's activities, rather than thinking about then when going to sleep or when you wake up.
- Increase exposure to bright light and sunshine during the day. This does not mean go out in the midday sun; rather in the mornings and afternoons, make sure you stand in the sun for a while. The natural sunlight enhances melatonin production in the evening; and vitamin D levels, which have been associated with insomnia and mood disorders when deficient.
- Avoid electromagnetic stress (EMS). This means keep alarm clocks away from the bed; avoid heated blankets; check cabling and transformer location. EMS can affect glandular function, and hence melatonin and serotonin levels.
- Avoid alcohol and drugs. The body needs to get into a sleep cycle naturally. Drugs and alcohol induce an unnatural sleep and become addictive. Alcohol often causes people to wake up later and not get back to sleep. Also, alcohol and drugs prevent much of the healing potential of sleep, as the body is dealing with the chemicals, rather than detoxifying.
- Don't drink fluids within two hours of going to bed. This will avoid the chances of waking up to use the bathroom.
- Take a hot bath or shower. Water has a relaxing effect and washes away the day's stresses.
- Keep the bed for sleeping. Avoid work and discussions which may increase your awareness.
- Buy a new mattress. Studies show approximately 60% people with mattresses 1-4 years old are likely to exercise the next day; whilst only 6-8% of people with a mattress 8-10 years old. Also, more people with newer mattresses were likely to get 7.5 hours or more sleep.